Hormonal imbalances can feel like an invisible force disrupting your energy, mood, and overall well-being. From stubborn fatigue and brain fog to frustrating menstrual cycles and stress that feels insurmountable, the symptoms are widespread and can significantly impact your quality of life. Modern diets and high-stress lifestyles often strip our bodies of the essential nutrients needed to keep our intricate endocrine system functioning correctly. Before considering complex solutions, the answer frequently lies in foundational, targeted nutrition.
This guide is designed to provide clear, actionable steps towards regaining control. We will explore the science behind the seven best vitamins for hormone balance, offering practical, evidence-based advice on how to use them effectively. Our focus is on empowering you with the knowledge to make informed decisions for your health.
You will learn not just what to take, but why specific vitamins are crucial and how to integrate them into your routine for maximum benefit. We will cover:
- The specific role each vitamin plays in hormone production and regulation.
- Optimal dosages based on current scientific understanding.
- Synergistic pairings that enhance absorption and effectiveness.
- Key factors to consider when purchasing high-quality supplements.
This comprehensive resource is your first step towards identifying nutritional gaps and using vitamins to help restore your body's natural equilibrium. Let's move beyond the symptoms and address the foundational needs of your hormonal health.
1. Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol)
Often called the "sunshine vitamin," Vitamin D3 is far more than a simple nutrient; it functions as a powerful steroid hormone within the body. Its influence on the endocrine system is profound, directly impacting the production of key sex hormones like testosterone and oestrogen, as well as regulating thyroid and adrenal function. A deficiency in Vitamin D is incredibly common, particularly in the UK, and is a significant, often overlooked, contributor to hormonal imbalances, mood disorders, and reproductive health issues. This direct hormonal role is why it tops our list as one of the best vitamins for hormone balance.
How Vitamin D3 Governs Hormonal Health
Vitamin D receptors are present on cells throughout the body, including in the ovaries, testes, pituitary gland, and hypothalamus, the core command centres of your hormonal network. When Vitamin D binds to these receptors, it triggers processes essential for hormone synthesis and signalling. For men, this can mean optimised testosterone production, while for women, it helps regulate menstrual cycles and supports ovarian function.
Key Benefit: Vitamin D3 acts as a hormone precursor, directly influencing the glands responsible for producing testosterone, oestrogen, and progesterone. It also supports insulin sensitivity, which is crucial for managing conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Practical Use Cases and Implementation
- For Low Testosterone: If you are a man experiencing symptoms of low testosterone (fatigue, low libido), correcting a Vitamin D deficiency can help boost free testosterone levels.
- For PCOS Management: For women with PCOS, supplementing with Vitamin D has been shown to improve insulin resistance, regulate menstrual cycles, and lower inflammation.
- For PMS and Mood Support: To reduce the severity of PMS symptoms like mood swings and cramps, ensure your D3 levels are adequate.
The following bar chart visualises the direct impact of therapeutic Vitamin D3 supplementation on testosterone levels in deficient men.
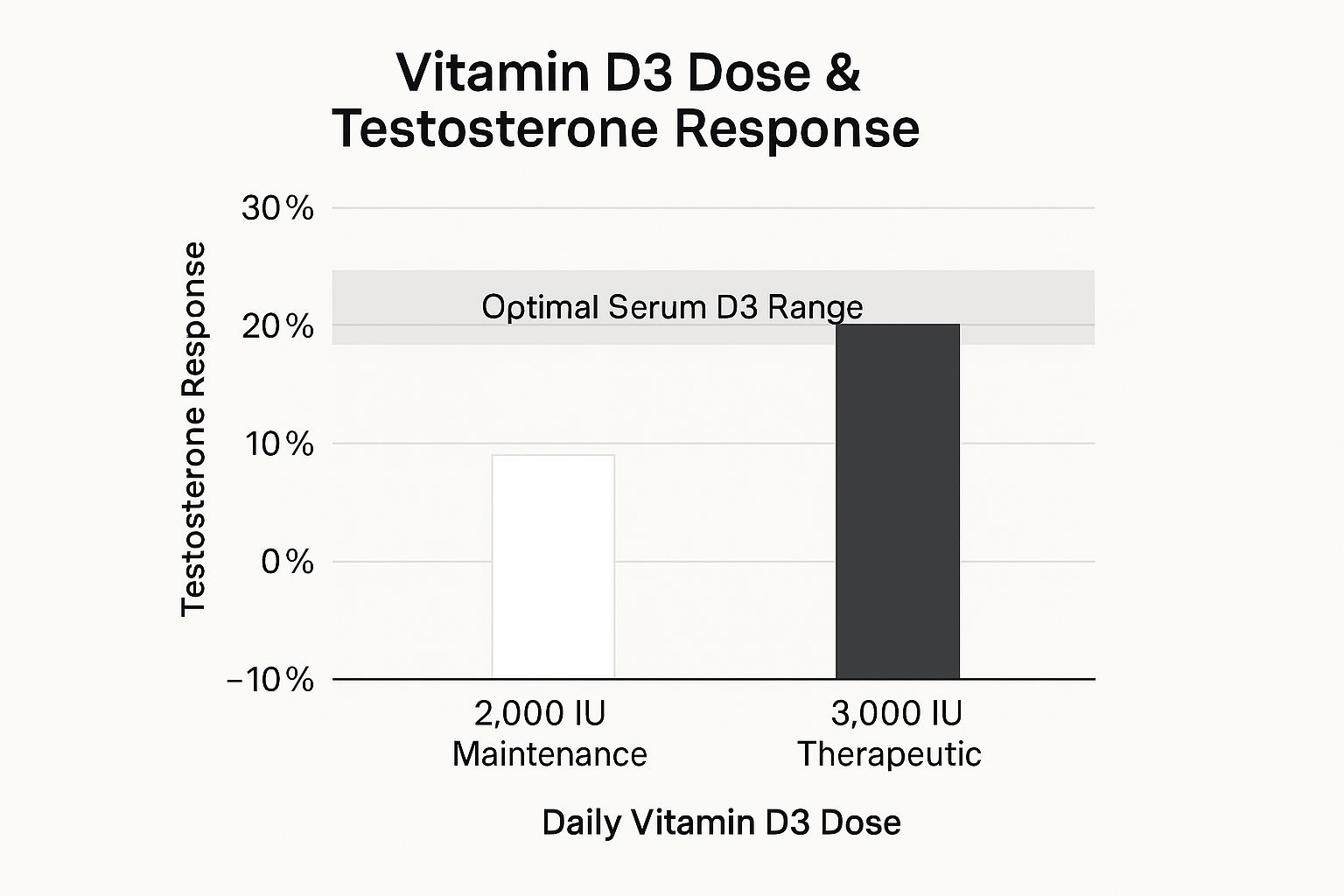
The chart clearly shows that a maintenance dose has little effect, whereas a higher therapeutic dose can lead to a significant 25% increase in testosterone.
Actionable Steps for Supplementation
- Get Tested: Before supplementing, request a 25-hydroxy vitamin D blood test from your GP to determine your baseline level. This is the only way to know your true status.
- Aim for Optimal Levels: Your target range for optimal hormonal health is 30–50 ng/mL (75–125 nmol/L).
- Dose Accordingly: If you are deficient, start with 2,000–4,000 IU daily. Your doctor can provide a personalised dosage based on your test results.
- Take with Fat: Vitamin D3 is fat-soluble. Always take your supplement with a meal containing healthy fats like avocado, olive oil, or nuts to maximise absorption.
- Pair with K2: Choose a supplement that combines D3 with Vitamin K2. This pairing is crucial for directing calcium to your bones, not your arteries.
- Re-Test: After 3-6 months of consistent supplementation, get re-tested to ensure you have reached the optimal range and can adjust to a lower maintenance dose.
2. B-Complex Vitamins (B6, B12, Folate)
The B-vitamin family is a group of eight water-soluble vitamins that work as a team to support energy production, brain function, and cellular metabolism. Within this group, Vitamin B6, B12, and Folate (B9) are particularly vital for maintaining hormonal equilibrium. They act as essential cofactors in countless biochemical reactions, including the synthesis and breakdown of key hormones and neurotransmitters, making them some of the best vitamins for hormone balance. Chronic stress, poor diet, and certain medications can rapidly deplete B-vitamin stores, leading to issues like adrenal fatigue, PMS, and poor oestrogen detoxification.

How B-Vitamins Govern Hormonal Health
B-vitamins are the workhorses of the endocrine system. Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) is crucial for producing progesterone and helps the liver process and clear excess oestrogen, a common driver of hormonal imbalance. Vitamin B12 (cobalamin) is fundamental for adrenal gland function and energy, while Folate is essential for methylation, a process that helps deactivate hormones and create neurotransmitters like serotonin, which heavily influences mood. Together, they ensure the entire hormonal communication network runs smoothly.
Key Benefit: B-vitamins support the liver's detoxification pathways, particularly for oestrogen, and are crucial for the production of progesterone and stress-coping adrenal hormones. They are also foundational for energy metabolism and mood regulation.
Practical Use Cases and Implementation
- For PMS Relief: To significantly reduce PMS symptoms like moodiness, irritability, and bloating, take up to 100mg of Vitamin B6 daily.
- For Adrenal Support and Fatigue: If you experience burnout or chronic fatigue, use a high-quality B-complex to support your stress response and energy levels.
- For Fertility and Oestrogen Dominance: To manage conditions like oestrogen dominance and improve fertility, support methylation pathways with Folate and B12.
Actionable Steps for Supplementation
- Choose Activated Forms: For superior absorption, look for supplements containing the "active" or "methylated" forms: pyridoxal-5'-phosphate (P5P) for B6, methylcobalamin for B12, and L-5-methyltetrahydrofolate (L-5-MTHF) for folate. This is especially important for those with MTHFR gene variations.
- Take with Food in the Morning: B-vitamins are energising. Take your B-complex supplement with breakfast to support your energy throughout the day and avoid potential sleep disruption.
- Use a Comprehensive Formula: A B-complex provides all eight B vitamins, which work synergistically. Don't just single out one unless advised by a healthcare professional. These vitamins often work best when paired with essential minerals; you can explore the benefits of trace minerals to understand how they support overall health.
- Split Your Dose: As B-vitamins are water-soluble, your body doesn't store them for long. For optimal blood levels, split your dose between the morning and early afternoon.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to your energy and mood. If you feel overly stimulated or anxious, you may need a lower dose or a non-methylated form. Start low and gradually increase the dosage.
- Consult a Professional: If you suspect a significant deficiency or have underlying health conditions, consult with a GP or a qualified nutritionist for personalised testing and dosing strategies.
3. Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid)
While widely celebrated for its immune-boosting properties, Vitamin C is a cornerstone nutrient for the endocrine system, particularly for adrenal gland function. The adrenal glands, which produce our primary stress hormone cortisol, contain one of the highest concentrations of Vitamin C in the body. This potent antioxidant is essential for synthesising cortisol and helps protect our hormonal glands from the oxidative damage caused by stress, environmental toxins, and normal metabolic processes. A chronic deficiency can impair the body's stress response, contributing to adrenal fatigue and widespread hormonal imbalance.

How Vitamin C Governs Hormonal Health
Vitamin C acts as a critical cofactor in the enzymatic reactions that convert cholesterol into steroid hormones, including cortisol, aldosterone, and adrenal androgens. Beyond the adrenals, it plays a vital role in supporting progesterone production, which is essential for regulating the menstrual cycle and sustaining a healthy pregnancy. Its powerful antioxidant capacity also shields hormones like testosterone and oestrogen from being degraded by free radicals, ensuring they can effectively communicate with their target cells.
Key Benefit: Vitamin C directly supports the adrenal glands in producing and modulating cortisol, helping the body adapt to stress. It also bolsters progesterone levels and protects all hormones from oxidative damage, making it one of the best vitamins for hormone balance.
Practical Use Cases and Implementation
- For Stress Management and Adrenal Support: During high-stress periods, take 1,000 mg of Vitamin C daily to help blunt cortisol spikes and reduce the physiological effects of stress.
- For Progesterone Support and PMS: If you have low progesterone, supplement with Vitamin C to help increase levels, regulate cycles, and correct luteal phase defects.
- For Enhanced Fertility: To improve both male and female fertility, use Vitamin C to protect sperm and egg cells from DNA damage.
Actionable Steps for Supplementation
- Start with Diet: Prioritise Vitamin C-rich foods like bell peppers, citrus fruits, kiwi, strawberries, and broccoli. However, therapeutic doses for hormonal support often require supplementation.
- Choose the Right Form: If standard ascorbic acid causes stomach upset, switch to a buffered form like magnesium ascorbate or calcium ascorbate, which are gentler on the digestive system.
- Divide Your Doses: Your body can only absorb a certain amount of Vitamin C at once. Split your intake into two or three smaller doses throughout the day (e.g., 500 mg in the morning and 500 mg in the evening) for better absorption and sustained blood levels.
- Dose for Your Needs: Start with a general maintenance dose of 500–1,000 mg daily. For high stress or to raise progesterone, you can increase to 2,000 mg daily. Start low and increase gradually.
- Pair with Bioflavonoids: Look for a supplement that includes citrus bioflavonoids like quercetin, hesperidin, or rutin. These compounds work with Vitamin C to enhance its antioxidant activity.
- Find Your Tolerance: The upper limit for Vitamin C is generally 2,000 mg per day. The most common side effect of taking too much is digestive upset. Find the dose that works for you without causing discomfort.
4. Vitamin E (Mixed Tocopherols)
Often overshadowed by other nutrients, Vitamin E is a crucial fat-soluble antioxidant that plays a specialised role in protecting the endocrine system. Its primary function is to defend cell membranes from oxidative stress, a key driver of hormonal disruption. This protective action is particularly vital for reproductive health, where it supports the glands responsible for progesterone production, shields the thyroid from damage, and helps mitigate the hormonal fluctuations associated with menstruation and menopause. As one of the most powerful fat-soluble antioxidants, its inclusion as one of the best vitamins for hormone balance is well-deserved.
How Vitamin E Governs Hormonal Health
Vitamin E’s antioxidant properties are central to its hormonal benefits. It neutralises free radicals that can damage endocrine glands like the ovaries, testes, and thyroid, ensuring they can produce and release hormones efficiently. For women, this translates to better progesterone synthesis during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, which is essential for menstrual regularity and fertility. It also helps manage inflammation, a common factor in hormonal symptoms.
Key Benefit: Vitamin E directly protects endocrine cells from oxidative damage, supporting progesterone production, reducing PMS severity, and easing menopausal symptoms like hot flushes. It also improves cellular response to hormones by maintaining healthy cell membranes.
Practical Use Cases and Implementation
- For Luteal Phase Support: If you have a short luteal phase or low progesterone, supplement with 400 IU of Vitamin E daily to help improve progesterone levels.
- For Menopausal Symptom Relief: To reduce the frequency and severity of hot flushes and night sweats, take a daily Vitamin E supplement.
- For Improved Fertility: For both men and women, use Vitamin E to enhance fertility by improving sperm quality and supporting uterine health.
Actionable Steps for Supplementation
- Choose the Right Form: Opt for a mixed tocopherols supplement (containing alpha, beta, gamma, and delta tocopherols) rather than one with only d-alpha-tocopherol. This provides a broader spectrum of antioxidant benefits. Look for natural forms (starting with "d-") over synthetic ("dl-").
- Dose Sensibly: A typical therapeutic dose for hormonal symptoms is 400 IU (268 mg) daily. Do not exceed this amount without consulting your GP, as high doses can interfere with blood clotting.
- Take with Fat: Like Vitamin D, Vitamin E is fat-soluble. Always consume it with a meal containing healthy fats, such as avocado, nuts, seeds, or olive oil, to ensure proper absorption.
- Time Your Intake: Avoid taking Vitamin E at the same time as an iron supplement. Iron can oxidise Vitamin E, reducing its effectiveness. Separate these supplements by at least a few hours.
- Increase Food Sources: Incorporate Vitamin E-rich foods into your diet, including sunflower seeds, almonds, spinach, and avocados, to support your levels naturally. For a deeper dive into antioxidant sources, you can learn more about the best antioxidant supplements for 2025 on myoji.co.uk.
5. Vitamin A (Retinol and Beta-Carotene)
Vitamin A is a critical fat-soluble nutrient that plays a foundational role in the endocrine system, yet it is often overlooked in discussions about hormonal health. It exists in two main forms: preformed Vitamin A (retinol), found in animal products, and provitamin A carotenoids (like beta-carotene), found in plants. The body converts carotenoids into retinol. Its influence extends from the thyroid gland to the reproductive organs, making it essential for the synthesis of sex hormones and the regulation of gene expression tied to hormone receptors. Inadequate Vitamin A status can disrupt this entire cascade, contributing to issues with fertility, thyroid function, and overall hormonal equilibrium.
How Vitamin A Governs Hormonal Health
Vitamin A is directly involved in the creation of pregnenolone, often called the "mother hormone" from which all other steroid hormones, including oestrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, are derived. It is also vital for thyroid health, as it helps the thyroid gland produce thyroid hormones and improves the body's ability to use them. Vitamin A receptors are present in the testes and ovaries, highlighting its direct role in reproductive processes and hormone production at a cellular level.
Key Benefit: Vitamin A is essential for the synthesis of nearly all steroid hormones and supports optimal thyroid function. It helps maintain the health of reproductive tissues and ensures that cells can properly respond to hormonal signals.
Practical Use Cases and Implementation
- For Thyroid Support: If you have symptoms of low thyroid function, even with normal lab results, optimise your Vitamin A intake to help convert the inactive T4 thyroid hormone to the active T3 form.
- For Menstrual Regularity: If you experience irregular cycles or heavy bleeding, correct a potential Vitamin A deficiency to help normalise your cycle and support progesterone production.
- For Male Reproductive Health: To maintain male fertility and hormonal vitality, ensure you have an adequate intake of Vitamin A to support testosterone and sperm production.
Actionable Steps for Supplementation
- Prioritise Food Sources: Incorporate a mix of retinol and carotenoid sources. Include liver, cod liver oil, eggs, and full-fat dairy for retinol. For beta-carotene, eat plenty of orange and leafy green vegetables like carrots, sweet potatoes, and spinach.
- Understand Dosage: The RDA is around 900 mcg (3,000 IU) for men and 700 mcg (2,333 IU) for women. Do not exceed 3,000 mcg (10,000 IU) daily of preformed retinol from supplements without medical supervision due to toxicity risk.
- Take with Fat: Vitamin A is fat-soluble. Consume it with a source of healthy fat, such as olive oil or avocado, to ensure it is properly absorbed by your body.
- Consider Conversion Factors: Be aware that your body's ability to convert beta-carotene to retinol can be influenced by genetics and gut health. If you are vegan or have digestive issues, you may be at higher risk for deficiency.
- Check Other Supplements: Many multivitamins and cod liver oil products contain Vitamin A. Always check labels and add up your total daily intake from all sources to avoid accidentally consuming an excessive amount.
6. Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone)
Often overshadowed by its counterpart, Vitamin K1, Vitamin K2 (menaquinone) plays a unique and critical role in hormonal health that extends far beyond blood clotting. Its primary function involves directing calcium to the right places, like bones, and keeping it out of the wrong places, like arteries and soft tissues. This calcium-regulating activity is profoundly linked to hormonal balance, especially during periods of hormonal fluctuation like menopause, making it one of the best vitamins for hormone balance support.
How Vitamin K2 Governs Hormonal Health
Vitamin K2 activates proteins, most notably osteocalcin and Matrix Gla Protein (MGP), which are essential for bone mineralisation and preventing arterial calcification. When oestrogen levels decline during menopause, bone density is put at significant risk. K2 helps mitigate this by ensuring the calcium you consume is effectively utilised for bone building. Furthermore, K2 works in a powerful synergy with Vitamin D3, enhancing its hormonal benefits and ensuring its safe use, particularly at higher therapeutic doses.
Key Benefit: Vitamin K2 optimises calcium metabolism, which is directly impacted by hormones like oestrogen. It supports bone density during menopause and works synergistically with Vitamin D3 to ensure hormones and nutrients are utilised effectively.
Practical Use Cases and Implementation
- For Postmenopausal Bone Health: To combat accelerated bone loss from declining oestrogen, supplement with K2 (specifically the MK-7 form) to improve bone mineral density and reduce fracture risk.
- For Cardiovascular Support: To support arterial flexibility and heart health during and after menopause, use K2 to prevent calcium buildup in the arteries.
- To Maximise Vitamin D Benefits: If you supplement with Vitamin D3 for any hormonal issue, add K2 to ensure the increased calcium absorption is channelled correctly, preventing potential long-term risks.
Actionable Steps for Supplementation
- Choose the Right Form: Opt for supplements containing Menaquinone-7 (MK-7). This form has a longer half-life in the body, making it more biologically active and effective than the MK-4 form.
- Dose Effectively: Take 90–120 mcg daily for maintenance and bone health support. Higher doses may be used therapeutically under professional guidance.
- Prioritise the D3/K2 Partnership: The synergy is non-negotiable. Choose a combined D3 and K2 supplement or take them together to ensure optimal hormonal and skeletal benefits.
- Take with Fat: K2 is fat-soluble. Always consume it with a meal that includes healthy fats such as olive oil, avocado, or nuts to ensure maximum absorption.
- Incorporate Food Sources: Boost your intake by eating K2-rich foods. The best source is natto (fermented soybeans), followed by hard cheeses, sauerkraut, and egg yolks.
- Consult Your GP if on Blood Thinners: If you take anticoagulant medications like Warfarin, you must consult your doctor before starting any Vitamin K supplement, as it can interfere with the medication's effectiveness.
7. Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid)
Often referred to as the "anti-stress vitamin," Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5) is a water-soluble B-vitamin that plays a fundamental role in adrenal health and hormone synthesis. It is an essential component of Coenzyme A (CoA), a molecule vital for a vast range of biochemical reactions, including the production of steroid hormones. Its primary function in hormonal health is supporting the adrenal glands, which produce cortisol and DHEA, making it indispensable for a healthy stress response and overall endocrine stability. This targeted adrenal support is why Vitamin B5 is one of the best vitamins for hormone balance, especially in our modern high-stress world.
How Vitamin B5 Governs Hormonal Health
Vitamin B5's influence stems from its direct involvement in the adrenal cascade. The adrenal glands require sufficient B5 to produce adequate levels of cortisol, the body's primary stress hormone. During periods of chronic stress, the demand for cortisol increases, which can deplete B5 levels and lead to adrenal fatigue or dysfunction. By providing the raw materials for hormone synthesis, B5 helps maintain a balanced stress response, preventing the downstream hormonal chaos that can affect everything from energy levels to skin health.
Key Benefit: Vitamin B5 is crucial for adrenal gland function and is a direct precursor for Coenzyme A, which is necessary to synthesise steroid hormones like cortisol. It helps the body adapt to stress, potentially reducing symptoms of adrenal fatigue and improving energy.
Practical Use Cases and Implementation
- For Adrenal Support and Stress: If you experience chronic stress or burnout, take B5 to help replenish depleted stores and support healthier cortisol output.
- For Hormonal Acne: To help reduce acne, consider high-dose Vitamin B5 supplementation, which may decrease oil (sebum) production by boosting Coenzyme A metabolism.
- For Enhanced Energy: To combat fatigue associated with hormonal imbalances, supplement with B5 to help improve stamina. It works well alongside other energy-supporting nutrients and practices. For a deeper look into this, learn more about adaptogens for energy from Myo-ji.
Actionable Steps for Supplementation
- Start with a B-Complex: For general support, begin with a high-quality B-complex vitamin to ensure you have a good foundation of all B vitamins working together.
- Consider Targeted Doses: For specific issues like adrenal fatigue or acne, a higher, standalone dose may be required. Start with a lower dose of 100–250 mg daily.
- Increase for High Stress: During intense or prolonged stress, take a therapeutic dose of 500–1,000 mg daily, split into divided doses, for more robust adrenal support. Always consult a healthcare professional before taking higher amounts.
- Take with Meals: To prevent potential stomach upset and enhance absorption, always take your Vitamin B5 supplement with food.
- Choose a Stable Form: Look for supplements containing calcium pantothenate or magnesium pantothenate, as these forms are known for their stability and bioavailability.
- Monitor Your Response: Pay close attention to your energy levels, stress tolerance, and skin health after 4-6 weeks of consistent use to gauge effectiveness and adjust your dosage if necessary.
Comparison of 7 Key Vitamins for Hormone Balance
| Supplement | Core Features / Characteristics | User Experience / Quality Metrics | Value Proposition 💰 | Target Audience 👥 | Unique Selling Points ✨ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin D3 (Cholecalciferol) | Fat-soluble hormone precursor, regulates 1,000+ genes | ★★★★☆ - Improves mood & testosterone | 💰 Affordable, requires monitoring | Adults with deficiency or hormonal imbalance | 🏆 Boosts testosterone by 25%, essential for endocrine support |
| B-Complex Vitamins (B6, B12, Folate) | Water-soluble cofactors in hormone synthesis | ★★★★☆ - Enhances energy & cognitive function | 💰 Moderate cost, daily intake required | Those with fatigue, PMS, stress | ✨ Methylated forms improve absorption, supports adrenal health |
| Vitamin C (Ascorbic Acid) | Water-soluble antioxidant, cortisol synthesis support | ★★★★☆ - Reduces cortisol & protects hormones | 💰 Low cost, multiple daily doses needed | People under stress, immune support seekers | ✨ Buffered forms reduce irritation, antioxidant protection |
| Vitamin E (Mixed Tocopherols) | Fat-soluble antioxidant, supports reproductive hormones | ★★★★☆ - Reduces menopausal symptoms | 💰 Moderate price, natural forms preferred | Women with hormonal cycle issues | ✨ Mixed tocopherols for broader antioxidant effect |
| Vitamin A (Retinol & Beta-Carotene) | Fat-soluble, essential for hormone & gene expression | ★★★★ - Maintains thyroid & reproductive health | 💰 Priced variably, risk of toxicity if overdosed | Hormonal balance, reproductive health seekers | ✨ Combines preformed & provitamin A for comprehensive support |
| Vitamin K2 (Menaquinone) | Fat-soluble, activates calcium metabolism proteins | ★★★★☆ - Supports bone & cardiovascular health | 💰 Higher cost, needed with vitamin D | Postmenopausal women, bone health focus | ✨ MK-7 form for longer activity, synergizes with D3 |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) | Water-soluble, essential coenzyme for steroid hormone synthesis | ★★★★ - Supports adrenal and stress response | 💰 Affordable, often included in B-complex | Stressed individuals, adrenal support | ✨ Key for cortisol production, improves stress tolerance |
Your Action Plan for Hormonal Balance
Embarking on the path to hormonal equilibrium is one of the most proactive decisions you can make for your health. Throughout this guide, we have explored the foundational roles that specific vitamins play in regulating your endocrine system. From the hormone-like actions of Vitamin D3 to the stress-moderating power of B-Complex vitamins, these micronutrients are crucial signalling molecules that direct hormonal traffic.
The journey to finding your balance is deeply personal. Your individual needs will depend on your lifestyle, diet, genetics, and current health status. Simply taking a supplement is not a magic bullet; the true value lies in a consistent, informed, and holistic approach.
Consolidating Your Knowledge into Action
Transforming knowledge into a tangible plan is simpler than it seems. The central theme is to move from passive reading to active implementation. Here is a structured, step-by-step approach to help you begin with confidence.
Step 1: Audit and Assess Your Current State
Before introducing any new supplements, take stock of where you are right now.
- Keep a Symptom Journal: For one to two weeks, log your daily energy levels, mood, sleep quality, and any physical symptoms. This creates a baseline to measure progress against.
- Review Your Diet: Honestly assess your current eating habits. Identify where you might be lacking in the vitamins we've discussed. Are you eating a variety of colourful fruits and vegetables, healthy fats, and lean proteins?
- Get Professional Testing: If possible, ask your GP or a nutritional therapist for a blood test to check your hormone and key vitamin levels (like Vitamin D or B12). This provides a clear, data-driven starting point.
Step 2: Prioritise and Implement Strategically
You do not need to start every vitamin at once. Based on your assessment, choose one or two priority areas.
- For General Stress and Energy: Start with a high-quality B-Complex supplement. These vitamins are water-soluble and crucial for adrenal function.
- For Immune and Thyroid Support: If you live in the UK, make Vitamin D3 a priority, especially during autumn and winter.
- Start Low, Go Slow: When introducing a new supplement, begin with the lowest effective dose. This lets you monitor your body’s response. Give it at least four to six weeks to observe any changes.
Step 3: Build a Supportive Lifestyle Foundation
Vitamins work with your daily habits, not in isolation. Create an environment where they can be effective.
- Prioritise Sleep: Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night. Hormonal regulation is profoundly tied to your sleep-wake cycle.
- Manage Stress: Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into your daily routine. This could be a 10-minute walk, deep breathing exercises, or time in nature.
- Nourish with Whole Foods: Eat a diet rich in fibre, healthy fats (like avocados and nuts), and lean protein. This helps to stabilise blood sugar, a cornerstone of hormonal health.
By following this action plan, you shift from being a spectator to being the director of your own health. Mastering these principles isn't just about feeling better today; it's about building a resilient body that can better navigate the stresses of modern life. The path to hormonal harmony is a continuous journey of listening to your body and adjusting your approach with intention and care.
To enhance your body's ability to utilise these vitamins and build a strong foundation for hormonal health, consider supporting your system at a cellular level. The trace minerals and fulvic acid in Oji Shilajit can help improve nutrient absorption and cellular energy production, creating the ideal internal environment for your new vitamin regimen to deliver maximum benefits. Discover how the power of ancient minerals can amplify your modern health strategy at Oji Shilajit.





